Paytm IPO: All you need to know

Incorporated in 2000, One97 Communications Limited is India’s leading digital ecosystem. The IPO of the parent company of Paytm opens for subscription between 8 and 11 November. Paytm’s public issue is likely to be India’s biggest IPO so far.
Here is everything you should know about the much-hyped Paytm IPO:
Offer details
-
IPO size: ₹18,300 crore
-
Fresh issue: ₹8,300 crore
-
Offer for sale: ₹10,000 crore
-
Price Band: ₹2,080-₹2,150 per share
-
Lot size: 6 shares
-
Cost per lot: ₹12,900
-
Issue opens: 8 Nov 2021
-
Issue closes: 10 Nov 2021
-
**Basis of allotment date:**15 Nov 2021
-
Initiation of refunds: 16 Nov 2021
-
**Credit of shares to demat account:**17 Nov 2021
-
Expected listing date: 18 Nov 2021
-
Registrar: Link Intime India Private Ltd
-
Contact: Mr. Amit Khera, Tel: +91 120 4770770
-
E-mail: compliance.officer@paytm.com
All shares will be listed at BSE (Bombay Stock Exchange) and NSE (National Stock Exchange).
Reasons for going public and objective of the IPO
-
Strengthening and growing the Paytm ecosystem through customer and merchant acquisition and retention
-
Providing its customers and merchants greater access to technology and financial services
-
Initiating strategic partnerships and investing in new business initiatives and acquisitions
-
Meeting the general corporate requirements
Key highlights
-
Incorporated in 2000, One97 Communications Limited is the parent company of Paytm.
-
It is India’s leading digital ecosystem for consumers and merchants
-
It offers a wide range of services, such as payments, commerce, cloud and financial.
-
As of June 30 2021, 33.3 crore consumers and over 2.1 crore merchants have registered with it.
-
Through its payment-led super app, the company provides innovative and intuitive digital products and services.
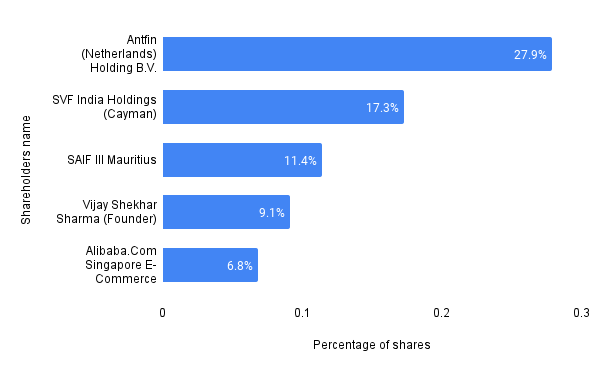
Company fundamentalsHere is some key fundamental information about the company:Five largest shareholders of Paytm
Financial information
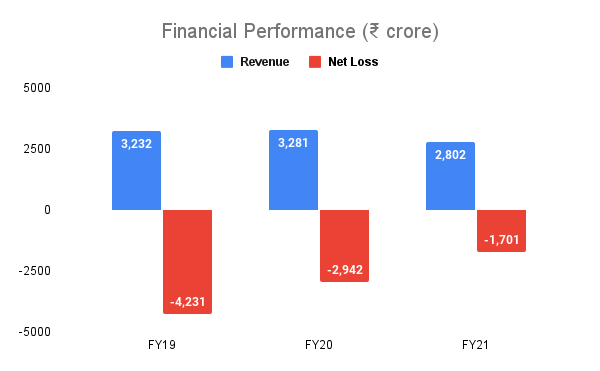
Over the past decade, the balance sheet has grown manifold. However, the primary reason for the losses is the company's continuous efforts in acquiring new clients and merchants. That said, Paytm has been making efforts to reduce its losses
Overview of business
Paytm started as a service for mobile top-ups and other utility bill payments. However, the company has aggressively expanded its service offering to create an all-encompassing digital payment ecosystem. Some of the most popular services available on the Paytm app include:
-
Flight, bus and train ticket booking
-
Investment platform (Paytm Money)
-
E-commerce platform for retail goods (Paytm Mall)
-
Interbank transfers and fixed deposits (Paytm Payments Bank)
-
Digital gold (Paytm Gold)
-
Insurance products (Paytm Insurance)
Strengths
-
First-mover advantage
-
One of the India’s leading and most trusted payment platforms
-
Strongtech focus approach
-
Each transaction provides insights into how Indians spend and save
-
Experienced management team
-
The all-encompassing financial services ecosystem
-
Strong brand identity
-
Wide customer and merchant base
-
Network effect leads to low acquisition costs and higher monetisation
Opportunities
-
Growing demand for fintech players such as Paytm
-
The surge in digitisation of finance is likely to work to the advantage of the company
-
The untapped potential of the consumer payment market in India
-
Expand into international markets
Threats
-
Cut-throat competition from domestic and global tech companies like Google Pay, PhonePe, MobiKwik, etc.
-
Growing concerns about the safety of online payments and financial transactions
-
Change in digital payments and online financial services rules and legal compliance parameters
Risks
-
A history of net losses
-
Economic slowdown due to the pandemic and other unexpected major market volatile events
-
Increase in payment processing charges to be paid to financial institutions and card networks
-
Pending litigations against the company, its subsidiaries and directors
-
Inability to form strategic partnerships or acquire new customers and merchants
-
Failure to innovate technologically
-
Dependency on third parties for some business verticals
-
Relying on mobile operating systems and application marketplaces
-
Any privacy or data security breach, cyber-attacks or internal misconducts