- home/
- stocks
Invest Right, Invest Now
Open a FREE* Demat and Trading account to invest in Stocks
By signing up you agree to our Terms and Conditions
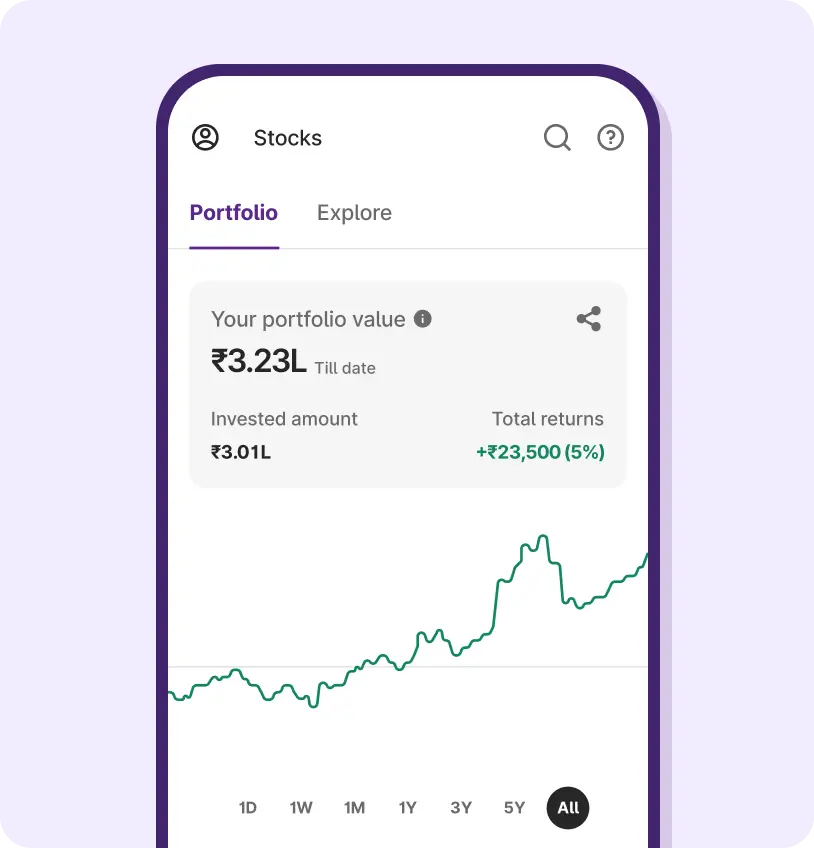
Discover Stocks Easily
5000+ stocks, find ‘the one’ easily with our smartlists
Place Quick Orders In A Few Clicks
One platform with many order types
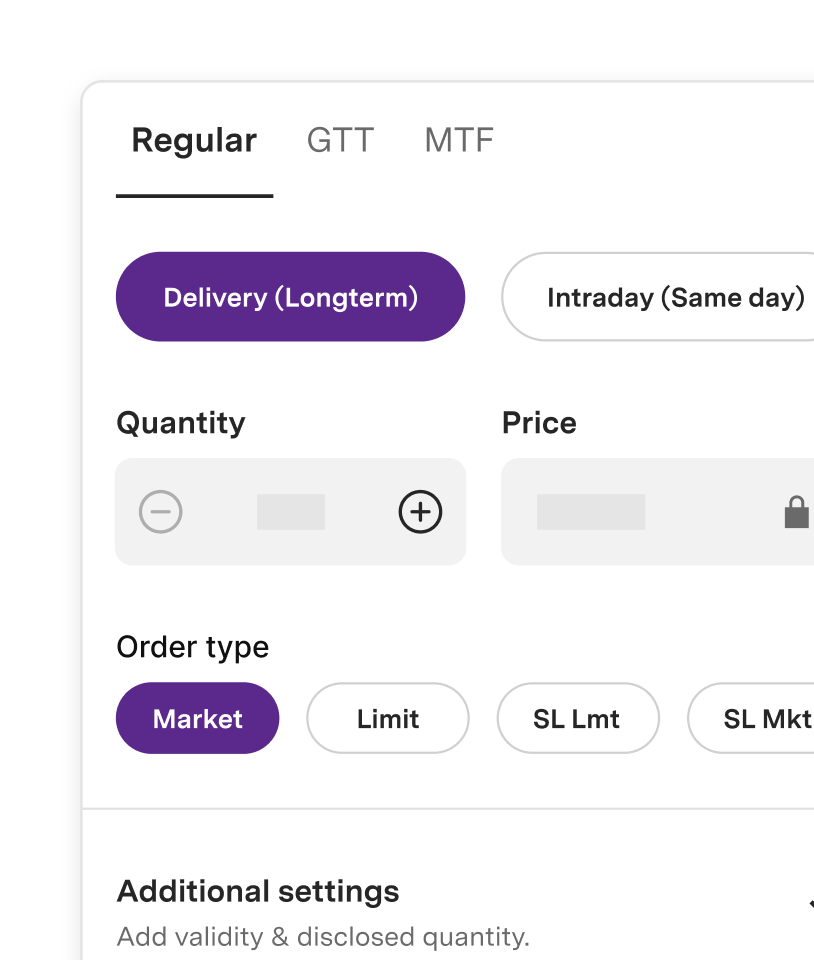
Delivery
Intraday
Good till Triggered (GTT)
Margin Trading Facility (MTF)
After-Market-Orders

Analyse Trends Confidently
5000+ stocks, find ‘the one’ easily with our smartlists
New to Buying Stocks?
You can do everything from a single frame
Discover stocks easily
With curated stock lists such as UpTrend, Best for Beginners, Everyday Brands, etc.
Invest in them confidently
With 6-point investment checklist and analyst ratings to buy, sell or hold a stock
Stock like you shop
Simplified buying and selling experience


Discover stocks easily
With curated stock lists such as UpTrend, Best for Beginners, Everyday Brands, etc.
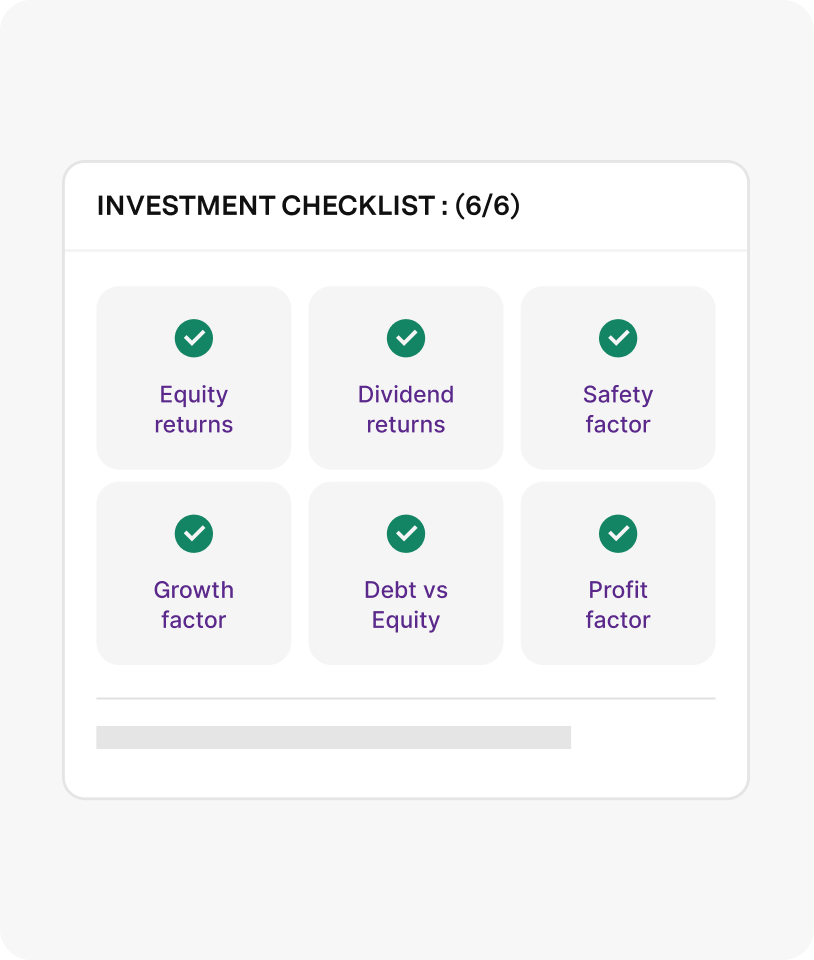
Invest in them confidently
With 6-point investment checklist and analyst ratings to buy, sell or hold a stock

Stock like you shop
Simplified buying and selling experience
Getting started with your investing journey?
From beginner to advanced, we cover all levels of learning