Option Strategy: Bull Call Spread
A bull call spread is a strategy that traders implement when they believe that the price of the stock or an index will rise moderately in the near future. In this strategy, a trader places two orders, one buy and one sell both of same expiry and same underlying.
Bull Call Spread setup📊
The strategy includes buying a call option at a lower strike price and selling a call option at a higher strike price.
The Bull Call Spread is a net debit strategy. Meaning, that after paying and receiving the premium for both call options, you start the strategy with net payout. Since the premium paid for buying the lower strike call option is higher than the premium received on selling the higher strike call option
- the strategy will be a debit spread.
Bull Call Spread example
Assume that NIFTY 50 is currently at 17,400. You believe that the index will moderately rise📈 before the expiry of the contracts. Here’s how the strategy pans out:
You buy a call option of 17,400 strike by paying a premium of ₹179.
(This is the lower strike)
Similarly, you sell a call option of 17,700 strike and receive a premium of ₹96.
(This it the higher strike)
Do note, the strikes selected should have the same expiry and same underlying.
(This is the lower strike)
Similarly, you sell a call option of 17,700 strike and receive a premium of ₹96.
(This it the higher strike)
Do note, the strikes selected should have the same expiry and same underlying.
As explained above, your net debit (premium paid) for this strategy is ₹83 (₹179
- ₹96). ( Premium paid for lower strike price
- premium received by selling a higher strike price).
Bull call spread payoff diagram
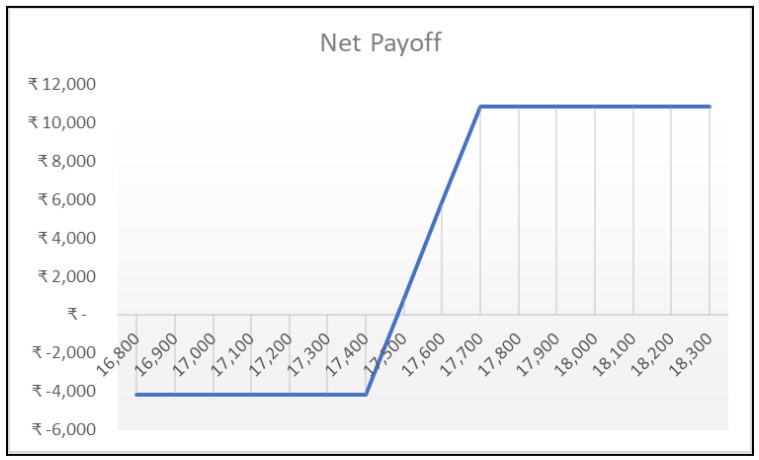
As you can see in the payoff graph above, the bull call spread clearly outlines the risk and reward once the trade is deployed. To understand this better, let’s dive deep into understanding the maximum gain and maximum loss potential of this strategy.
Break even point🚦
Aka the point at which strategy makes no profit or loss.
Aka the point at which strategy makes no profit or loss.
To calculate the breakeven point of this strategy, add the strike price of the lower call option to the net premium paid i.e 17,400 +83= 17,483. In simpler terms, if the NIFTY 50 closes above the 17,483 at expiry, the strategy will make a profit. If it closes at 17,483, then the strategy will neither make a profit nor a loss.
Maximum profit
The maximum profit for this strategy is limited to the width of the spread minus the premium paid. Meaning, to calculate the width of the spread we have to subtract higher call option strike from lower call option strike. Here’s how it works:
The maximum profit for this strategy is limited to the width of the spread minus the premium paid. Meaning, to calculate the width of the spread we have to subtract higher call option strike from lower call option strike. Here’s how it works:
Width of the spread is 300 points (17,700-17,400)
Net premium paid is ₹83.
Maximum profit turns out to be ₹217 (300–83), that is ₹10,850 [(217*50 lot size)]. It is to be noted that the lot size of an options contract for the NIFTY 50 index is 50.
Net premium paid is ₹83.
Maximum profit turns out to be ₹217 (300–83), that is ₹10,850 [(217*50 lot size)]. It is to be noted that the lot size of an options contract for the NIFTY 50 index is 50.
Maximum loss
While deploying this strategy, we have paid a net premium of ₹83. Since bull call spread is a net debit strategy, the risk is defined to the extent of the premium paid. This means that debit or premium paid is the maximum risk of the trade, i.e ₹4,150 [(83*50 lot size)]. It is important to note, that the strategy will make a loss, if the NIFTY 50 closes below the breakeven point at expiry.
While deploying this strategy, we have paid a net premium of ₹83. Since bull call spread is a net debit strategy, the risk is defined to the extent of the premium paid. This means that debit or premium paid is the maximum risk of the trade, i.e ₹4,150 [(83*50 lot size)]. It is important to note, that the strategy will make a loss, if the NIFTY 50 closes below the breakeven point at expiry.
In a nutshell💰Risk
The risk of the strategy is defined to the extent of the premium paid, i.e is ₹4,150 (83*50).
The risk of the strategy is defined to the extent of the premium paid, i.e is ₹4,150 (83*50).
Reward
The width of the spread is 300 and the net premium paid is ₹83. So, the maximum profit for this strategy turns out to be ₹217 (₹300-₹83), that is 10,850. (217*50)
The width of the spread is 300 and the net premium paid is ₹83. So, the maximum profit for this strategy turns out to be ₹217 (₹300-₹83), that is 10,850. (217*50)
Deploying a Bull Call Spread strategyWhat works in favour
-
The potential loss is reduced as the net premium outflow by combining both legs is lower than a single buy order.
-
By selling the higher strike call option, the risk of the strategy gets capped to a certain extent.
-
Strategy benefits from gradual rise in implied volatility (IV). Simply put, the strategy is initiated when the IV is low and is expected to rise.
What works against
-
Time value (Theta) of the lower strike( buy call option), works against the strategy and decreases everyday.
-
Overall margin required is slightly higher than the single-leg buy order.
-
By selling the higher strike call option, the overall profit of the trade gets capped.
-
The strategy is not initiated when the implied volatility is high and is expected to decline. Meaning, once the trade is initiated, a crush in IV can lead to fall in option premiums.
We hope this strategy was simple and easy to understand. You can try spotting it on the option chain on Upstox and see if you are able to identify levels.
Want a pre-curated Bull Call Spread strategy? Upstox has introduced Ready-made Option Strategies, a safer way to trade in NIFTY 50 and BANK NIFTY options. Click here to know more.