EBITDA: Meaning, Formula, Margin, & How to Calculate
Written by Mariyam Sara
Published on October 08, 2025 | 2 min read
You often must have heard the word ‘EBITDA’ on SharkTank. EBITDA is an important financial metric that represents the strength of a company. It is a crucial factor of fundamental analysis. If you are a novice investor, the EBITDA is the first metric you need to learn about.
In this blog, you will learn what EBITDA is, its formula, EBITDA margin, and how to calculate it.
What is EBITDA?
EBITDA means ‘Earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation & amortization’. It is also known as ‘Operating Profit’, as this metric tells you how much profit the company has earned from its core operation.
It excludes interest expenses, tax, and depreciation and gives a true picture of the company’s profitability.
Formula
Most companies’ annual reports have EBITDA already calculated, but some may not, so it's best to learn to calculate it yourself. Here’s how you can calculate EBITDA,
EBITDA = Net income + Taxes + Interest + Depreciation & Amortization.
Following is TVS Motors LTD’s Profit & Loss statement for the Financial Year 2023-2024. Let’s find out its EBITDA margin.
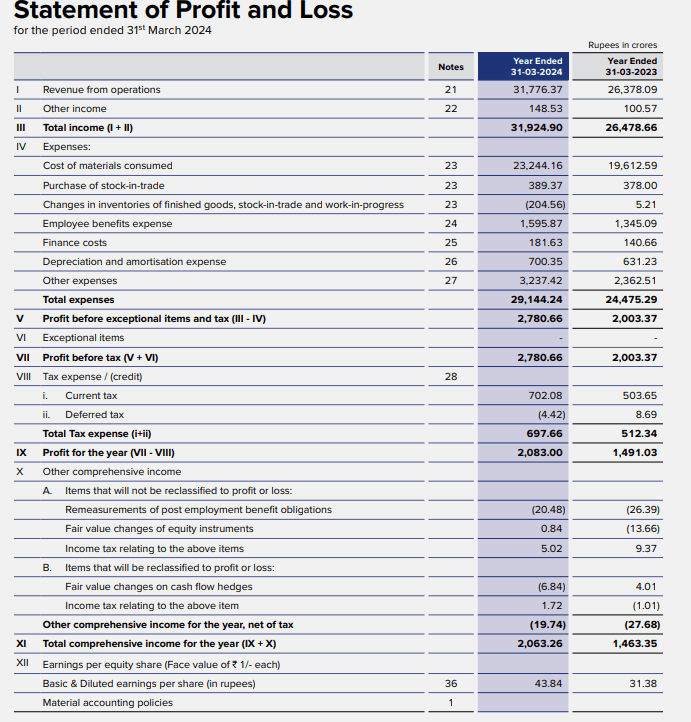
Substitute the values in the formula,
EBITDA = 2083 + 181.63 + 697.66 + 700.35
(Do note that in annual reports, interest payments are often termed as ‘Finance costs’).
EBITDA = 3,662.64 (In crores)
What is EBITDA margin?
EBITDA margin shows what percentage of a company’s revenue is represented by its EBITDA. Use this formula to calculate EBITDA margin.
EBITDA Margin = EBITDA / Aggregate Earnings.
Now let’s find out the EBITDA Margin = EBITDA / Aggregate earnings
= 3662.64 / 31,776.37 x 100
EBITDA Margin = 11.43%
You can compare TVS Motors’ EBITDA margin with its peers to analyze its financial performance. The company with average or above-average EBITDA is favorable to investors.
Why knowing EBITDA is important for investors
Here’s why every investor should look at a company’s EBITDA before investing.
Profit-making capability from core operations
EBITDA shows the capability of a firm to generate profit from its core operations. It aids investors in making informed investment decisions.
Facilitates peer-to-peer comparison
EBITDA helps investors compare a company’s profit-generating capability to its peers to analyse whether it’s performing well or not, as per industry standards.
Assess debt-paying capability
When a company applies for a loan, the lenders look at the EBITDA-to-interest coverage ratio, which shows the company’s ability to cover its interest payments. A high ratio represents solid financial stability.
The formula for EBITDA-to-Interest ratio = EBITDA / Interest Expenses (also known as Finance cost).
Try finding out the EBITDA-to-Interest ratio of TVS Motors by using the figure given in the Profit & Loss statement above.
Limitations of EBITDA
The following are the limitations of EBITDA,
EBITDA is a powerful financial metric used to analyse a company’s profitability and should be used by all investors. However, it is best to use EBITDA along with other financial metrics to get a clearer picture of a company’s financial performance. EBITDA may vary by industry, so find out the average EBITDA of an industry when fundamentally analyzing a company.
About Author
Mariyam Sara
Sub-Editor
holds an MBA in Finance and is a true Finance Fanatic. She writes extensively on all things finance whether it’s stock trading, personal finance, or insurance, chances are she’s covered it. When she’s not writing, she’s busy pursuing NISM certifications, experimenting with new baking recipes.
Read more from MariyamUpstox is a leading Indian financial services company that offers online trading and investment services in stocks, commodities, currencies, mutual funds, and more. Founded in 2009 and headquartered in Mumbai, Upstox is backed by prominent investors including Ratan Tata, Tiger Global, and Kalaari Capital. It operates under RKSV Securities and is registered with SEBI, NSE, BSE, and other regulatory bodies, ensuring secure and compliant trading experiences.