Introduction to the Bear Call Spread
Introduction to the Bear Call Spread
If you are bearish on a stock or index there are a few ways that you can execute an options trading strategy. You could buy a put or enter into a bear put spread. Both of these strategies are debit strategies or trades that require an initial cash outlay. Both of these strategies also benefit from a downward price movement in the underlying asset. Instead, what if you wanted to still benefit from a downward price movement but didn’t want to have an initial cash outlay? This is where the bear call spread comes in. This option strategy provides a comparable payoff outcome as the bear put spread but is a credit strategy – a trade that provides you with a cash inflow on entry. Let’s discuss how this option strategy works.
How do you construct a long bear call spread?
To construct a bear call spread you need to short a call option that is in-the-money. A short call option is an inherently bearish position, but due to the risk of unlimited losses, you will hedge this by purchasing an out-of-the-money call option. The long call option will limit the losses. The credit received from shorting the in-the-money call option will be greater than the cost of purchasing the out-of-the-money call option. This will result in a net credit to enter into the long bear call spread.
Illustration 1
 Source: Upstox
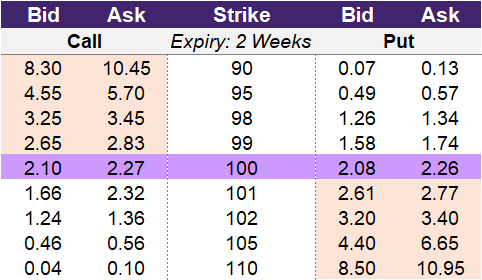
Source: UpstoxUsing the data in illustration 1 we can construct an example bear call spread. Assume that you are slightly bearish on this stock and think that it could possibly fall 1% prior to expiry. You select the 99-strike price to short. This will provide you a credit of 2.65. To hedge this short call you decide to purchase the 105-strike price. This will cost you 0.56. You could also select other strike prices like the 101 or 102-strike. These would provide more protection from an upward movement but would cost more. However, you are confident in the downward 1% move, so your 105-strike purchase will result in a net premium collected of 2.09 (2.65 – 0.56).
Why would a trader use a bear call spread?
A trader would enter into a bear call spread if you are bearish on the underlying stock or index. In addition, you prefer to collect a premium instead of paying upfront to enter into the trade. Lastly, you are comfortable with capping both your gains and losses unlike a put option that has significant potential gains.
What is the max profit of a long bear call spread?
Key Formula:
- Long Bear Call Spread Max Profit = Initial Net Credit (Premium) Received
For a bear call spread, the maximum profit that you can make is the net premium you initially receive from entering into the strategy. In our example from illustration 1, you entered into the 99-105 bear call spread. This allowed you to collect a net premium of 2.09. This 2.09 is the most you can make from this trade.
How much can you lose trading a long bear call spread?
Key Formula:
- Long Bear Call Spread Max Loss = Lower Strike (short call) – Upper Strike (long call) + Net Premium Received
- Net Premium Received = Credit from Short Call – Debit from Long Call
A bear call spread has capped losses because you purchase a call option that hedges the short option position. To calculate the max loss for this strategy, you take the difference between the lower strike price and the higher strike price and add the net premium collected. Using our prior example from illustration 1, you sold the 99-strike price and purchased the 105-strike price. You collected a net credit of 2.09. Therefore, the max loss for this example bear call spread is -4.91 (99 – 105 + 2.09).
What is the breakeven point when entering a long bear call spread?
Key Formula:
- Long Bear Call Spread Breakeven Point = Lower Strike Price (Short Call Strike Price) + Net Premium Received
- Net Premium Received = Credit from Short Call – Debit from Long Call
The breakeven point for the bear call spread is calculated by adding the net premium collected to the lower strike price. The lower strike price of the bear call spread is the short call strike price. To calculate the net premium, you take the difference between the credit received by selling the call option and the amount paid to enter into the long call. Going back to our example, the short call strike price was 99 and the net premium collected was 2.09. This means that the breakeven point for our example bear call spread is 100.09. If the underlying stock is above 100.09 on expiry, then this trade will be a loss. If the underlying stock is below 100.09 on expiry, then this trade will be profitable.
What is the profit formula for a long bear call spread?
Key Formula:
- Long Bear Call Spread Profit = Net Premium Received + Max(0 Underlying Price – Upper Strike Price) – Max(0 Underlying Price – Lower Strike Price)
- Net Premium Received = Credit from Short Call – Debit from Long Call
The profit formula for a bear call spread is a combination of the initial net premium received from entering into the strategy as well as the payoff of the individual option contracts – the short call and long call.
What is the payoff diagram for a long bear call spread?
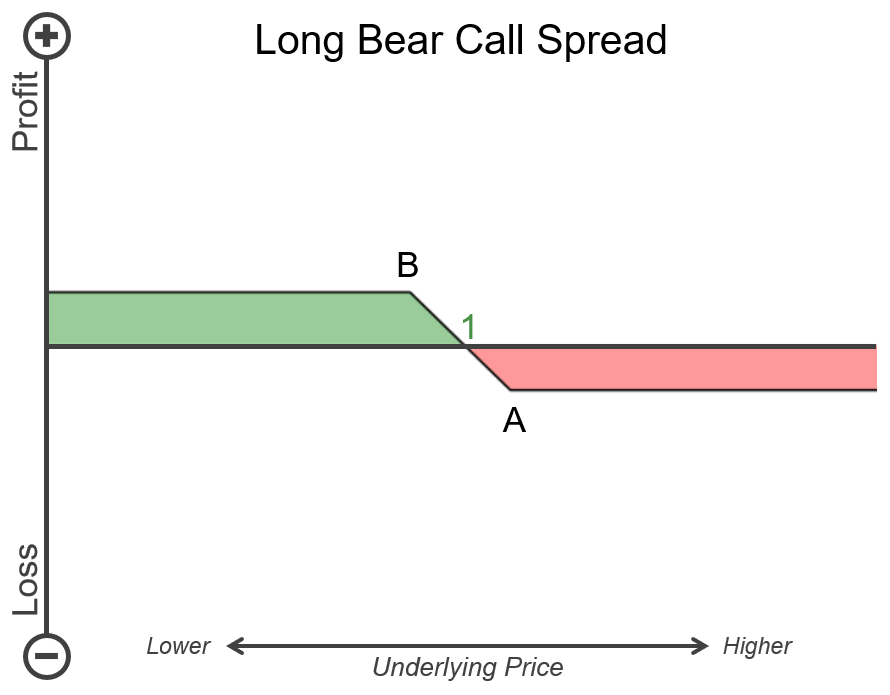
The payoff diagram for the bear call spread is displayed in illustration 2. Point B is the strike price of the short call option. Point A is the strike price of the long call that acts as the hedge for the short call option. Point 1 represents the breakeven point for the strategy. The horizontal axis is the price range of the underlying asset. Higher prices are to the right, while lower prices are to the left. The section in green represents profit, and the section in red represents losses. As the price of the underlying asset falls or moves from the right to left on the chart, you can see that the strategy becomes profitable.
Illustration 2
 Source: Upstox
Source: UpstoxWhat is the point of max profit for a long bear call spread?
Key Formula:
- Price of Underlying <= Lower Strike Price (short call strike)
The point of max profit for the bear call spread is when the underlying price is at or below the lower strike, which is the short call strike price. Since the bear call spread is a bearish strategy, as the underlying falls in price, the strategy will perform better. In our prior example, you shorted the 99-strike price because you believed that the stock would fall by 1%. This means that if the underlying is at 99 or below on expiry, this example bear call spread will attain the max profit.
What is the point of max loss for a long bear call spread?
Key Formula:
- Price of Underlying >= Upper Strike Price (long call strike)
The max loss for the bear call spread occurs when the underlying price rises to the upper strike price – the long call strike price – on expiry. The long call option as part of the bear call spread acts as a hedge against the short call option. Therefore, the long call option caps the loss potential. In our example, the long call strike price was 105. So, if the underlying stock is at or above 105 on expiry, then this strategy will have the max loss.
What is the difference between buying a bear call spread and a bear put spread?
A bear call spread and bear put spread provide the same outcomes. If you look at the payoff diagrams for these two strategies, you will see that they are identical. A trader would prefer the bear call spread over the bear put spread if they prefer to receive an upfront credit instead of paying a debit to enter into the strategy. In addition to this, there could be slight differences in the max gain, max loss, and risk-reward ratios simply based on market liquidity.
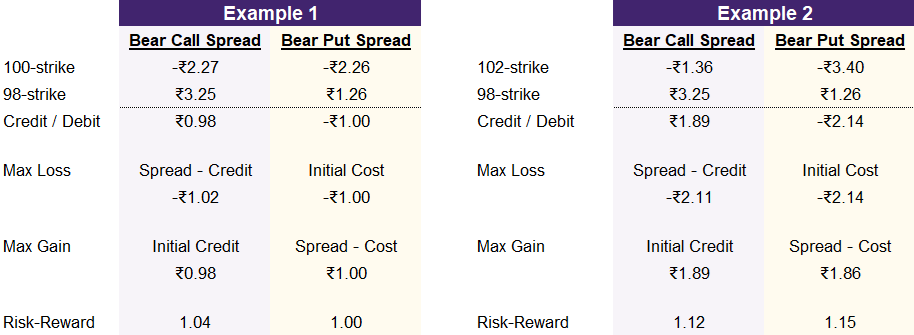
In illustration 3, we have two example comparisons. In example 1, we compare a bear call spread and bear put spread with the same strike prices: 99 and 100. In this example, you can see that the bear put spread has a slightly lower max loss and slightly higher max gain. This is due to the liquidity of the strikes for the bear call spread.
In example 2, we see the opposite. Here, we are comparing a bear call spread and bear put spread with 99 and 102-strike prices. In this case, the bear call spread has the lower max loss and higher max gain. This leads to the bear call spread having the more favorable risk-reward ratio. Again, the slight differences are due to market liquidity.
Illustration 3
 Source: Upstox
Source: UpstoxSummary
- A bear call spread is used when you believe that the underlying stock or index will fall in price.
- This strategy performs best if the decrease in price isn’t significant because a large price change is more beneficial to a long call strategy than a bear call spread.
- The bear call spread is a credit strategy.
- This strategy has a fixed max gain and max loss.
- The max gain is the initial credit received.
- A comparable strategy to the bear call spread is the bear put spread. However, the bear put spread is a debit strategy that requires an initial cash outlay.
Is this chapter helpful?
- Home/
- Introduction to the Bear Call Spread