Opting for Options
Why you should consider opting for Options?
Options are an essential tool in a trader’s arsenal. In this chapter, we will compare equity, futures, and options on various key parameters to help you learn about options and its utility to a trader.
Trend suitability
If you analyze the Nifty 50 historical data, you will see that it does not always move up. Recent data indicates that on average, five months in a year, the market is either trending down or moving sideways.
Illustration 1: Nifty50’s movement
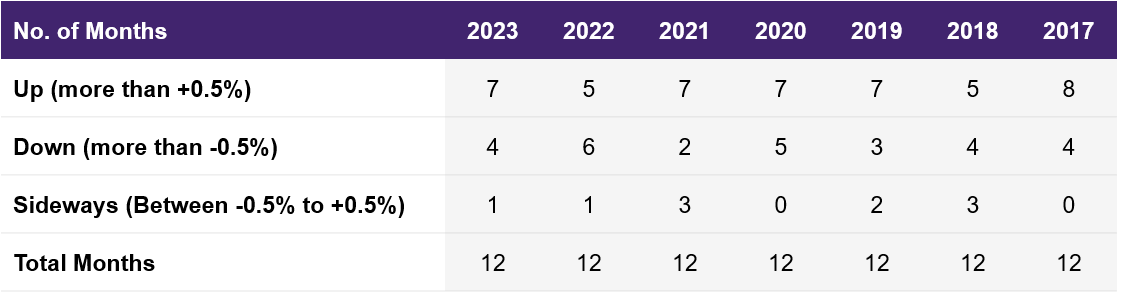 Source: NSE
Source: NSEIt means that trading only in equity shares may not always work. When you trade equity shares, you only profit when the share price moves up. If you believe the stock price will go down, your only option is to sell the shares before the price goes down. Here, we are not discussing intraday trading or the profit from dividends.
With futures, a derivative instrument like options, you only profit when the market moves up or down. So, unlike stocks, you can profit from a downward movement in a stock price. But with futures, you can’t profit if the market is moving sideways or is flat.
Illustration 2: Options: A ‘friend for every trend’
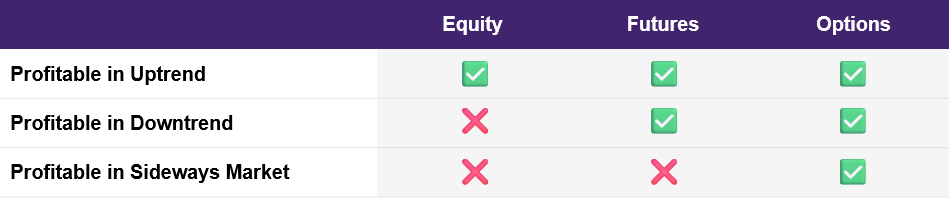 Source: Upstox
Source: UpstoxNote: We are not considering intraday equity trading for this discussion.
In contrast, options give a trader tremendous flexibility and can potentially deliver profits whether markets are trending up, down, or sideways.
Capital requirement
Options are also extremely capital efficient and deliver higher returns on investment than other instruments. Let’s see this with an example.
Let’s say you believe that Reliance Industries could rise from ₹3,000 to ₹3,100 in the next month. To benefit from this, you could buy Reliance shares or Reliance Options. To buy a lot size of 250 shares at ₹3,000, the capital requirement would be ₹7,50,000. To buy the minimum lot size of 250 options at a market price of, say, ₹60, the capital requirement would be only ₹15,000.
Illustration 3: Options have a low capital requirement
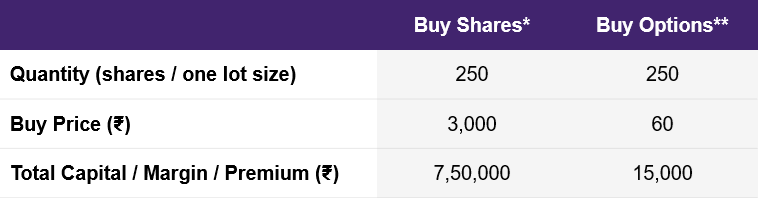 Source: Upstox
Source: UpstoxShares bought without margin trading facility (MTF). Reliance 3000-strike call option.
Return on investment (ROI)
You expected Reliance to rise to ₹3100, and it did! Since your target has been met, you decide to close your position. Here is how the profit and return on investment, or ROI, under shares and options would be:
You make a profit of ₹100 per share, or ₹25,000 by selling 250 shares. That’s a 3.3 percent ROI on your initial capital of ₹7,50,000.
The market price of the Reliance Industries options, during the same time has risen to ₹100. So, you make a profit of ₹40 per option or ₹10,000 on the lot size of 250 options. That’s approximately a 67 percent ROI on your initial capital of ₹15,000.
Illustration 4: Options could deliver very high ROI
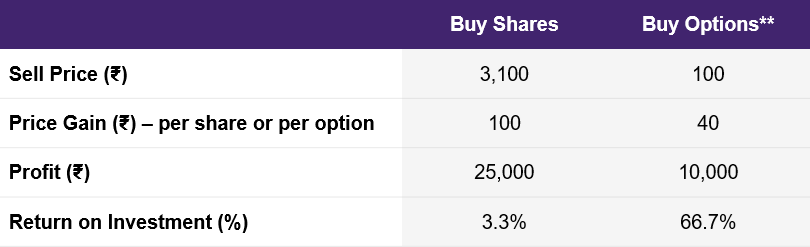 Source: Upstox
Source: UpstoxCash value on expiry of 3000 strike call option
While a 67 percent return in a month from options trading looks astonishing, it is possible. Successive winning trades can also have a strong compounding effect on your capital. But high returns come with high risk. There’s a fair chance you could lose the entire premium invested. For example, had Reliance closed below ₹3000, which is the strike price of the option purchased, you would have lost the entire premium of ₹15,000 that you paid. What if Reliance only went up a little to ₹3,050? The option would be worth ₹50 on expiry which is less than the ₹60 that you paid for it. In this example, a 1.7% gain in stock still resulted in a 17% loss on the options trade.
Pre-defined payoffs
With most options strategies, you can cap your returns in profit and loss. This helps in two ways.
- You know the exact risk and reward before taking the trade.
- In the event of a big gap-up or gap-down opening, the payoffs won’t change. More importantly, the losses will be capped. In contrast, the losses could be dramatic in equity or futures positions in such a scenario.
To Conclude:
Options can potentially deliver profits in a bull market, a bear market and even when the market moves sideways.
As compared to shares or futures, options have a low capital requirement and deliver a higher return. These high returns come with high risk. One could potentially lose the entire capital. Options strategies enable you to know the exact risk and reward before taking the trade.
What it means is that if you are able to control the risks associated with options, you could potentially trade in any market situation with lower capital and can generate high returns on your capital. Sounds too good to be true? Well, it isn’t. But it comes with a learning curve. That said, we are here to help you get your basics in place.
Is this chapter helpful?
- Home/
- Opting for Options