Short Call Ladder Options Strategy
Written by Upstox Desk
Published on July 31, 2025 | 5 min read

Short Call Ladder options strategy is also known as Bear call ladder strategy. It is a three-legged strategy that is implemented when the market outlook is outright bullish with an expectation of significant expansion in volatility. The strategy does incur a limited loss when prices fall to a limited extent. But the strategy can deliver profit even when prices continue to fall, in case of unexpected sell off.
The Short Call Ladder is also an improvement over the popular Bear Call spread . It extends the Bear Call spread by adding an additional leg. The structure is implemented by selling one ITM call option to collect premium, buying one ATM call option at higher strike and buying yet another OTM call option further up the chain, giving an impression of a ladder. The strikes may or may not be spaced equally among themselves but all the strikes are required to have a common underlying and expiration date.
The spread generally has a net credit as selling ITM call option would fetch maximum premium. The long ATM and OTM calls shall always be priced cheaper as they possess no intrinsic value.
Illustration:
The Nifty is currently at 18,000.
| Strategy | Index | Action | Strike | Premium |
| Short Call Ladder | Nifty50 | Sell Call | 17,900 (strike 1) | 160 |
| Buy Call | 18,000 (strike 2) | -90 | ||
| Buy Call | 18,100 (strike 3) | -50 | ||
| Net Premium | 20 |
The sold ITM call premium is the highest among all three call options. Selling the ITM call fetches the most premium, thereby turning the spread into the net credit. The net premium received is instrumental in reducing the overall cost outlay of the strategy.
This strategy has two breakeven points.
Lower breakeven point = (strike 1 + net premium) = 17,900 + 20 = 17,920 Upper breakeven point = (strike 3 + strike 2 -strike 1 – net premium received) = (18,100 + 18,000 – 17,900 – 20) = 18,180
Max potential loss = (strike 2 – strike 1 – net premium received) * Lot size = (18,000 – 17,900 – 20) * 50 = ₹4,000
Max profit on upside = Unlimited Max profit on downside = (Net premium received * lot size) = 20 * 50 = ₹1,000
The Short Call Ladder or Bear Call Ladder is essentially a bullish strategy, which can benefit the holder in case of unforeseen sell off. One should not be misled by the name of the strategy. The spread results in potential unlimited profit when the prices rise above the upper breakeven point and when the prices move below the lower breakeven point, the holder is still able to preserve the net premium that was collected upfront while deploying the strategy.
When prices stagnate between the two short call options, the spread will incur its maximum loss. When the price remains range bound, the long call options shall expire worthless and the holder will have to forfeit all the premium paid, thereby resulting in a limited loss.
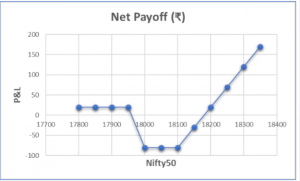
Payoff Schedule
Nifty50 @ Expiry | Net Payoff (₹) |
17800 | 20 |
17850 | 20 |
| 17900 | 20 |
17950 | -30 |
| 18000 | -80 |
| 18050 | -80 |
18100 | -80 |
| 18150 | -30 |
18200 | 20 |
| 18250 | 70 |
18300 | 120 |
| 18350 | 170 |
Payoff chart
Impact of Greeks:
-
The short call option is ITM, and possesses the highest intrinsic value. Therefore, it would not be easily affected by time decay. On the contrary, the ATM and OTM long call will face time decay and experience premium erosion at faster rate, especially when spread nears expiry. Therefore, the Theta has a negative impact.
-
The strategy is based on rapid price acceleration, which can only be possible when there is significant increase in volatility. Thus, Vega has a positive impact.
Conclusion:
-
The Short Call Ladder options strategy is easy to implement and manage, as the holder of the spread is protected against facing any kind of unlimited losses.
-
Though it is called a Short Call Ladder, one must never assume it as a bearish strategy. On the contrary, it is a bullish strategy that provides a small sustenance profit when the prices fail to rally upwards.
-
Keeping this in mind, one must never initiate this strategy to earn profit from down move.
A trader or investor would need a significantly small amount of margin to initiate the spread. As short and long call option positions provide adequate hedge against each other and additional long call positions are created by paying a small premium value.
About Author
Upstox Desk
Upstox Desk
Team of expert writers dedicated to providing insightful and comprehensive coverage on stock markets, economic trends, commodities, business developments, and personal finance. With a passion for delivering valuable information, the team strives to keep readers informed about the latest trends and developments in the financial world.
Read more from UpstoxUpstox is a leading Indian financial services company that offers online trading and investment services in stocks, commodities, currencies, mutual funds, and more. Founded in 2009 and headquartered in Mumbai, Upstox is backed by prominent investors including Ratan Tata, Tiger Global, and Kalaari Capital. It operates under RKSV Securities and is registered with SEBI, NSE, BSE, and other regulatory bodies, ensuring secure and compliant trading experiences.