are investing in their dreams.

Upstox for Investors
Invest Right, Invest Now in Stocks, Mutual Funds, and IPOs
Investment Ideas
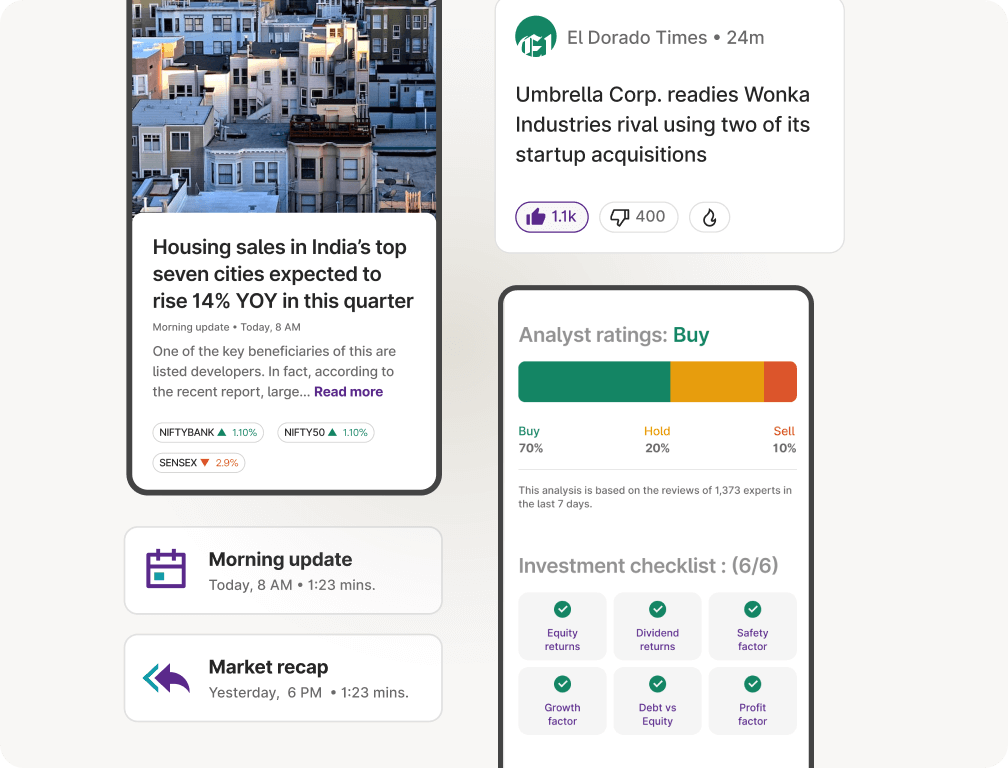
News & Insights
Order Placement
Top rated Funds | Best for Beginners | Top 30 actively traded Stocks

Analyst ratings | Investment checklist | Risk & return related info
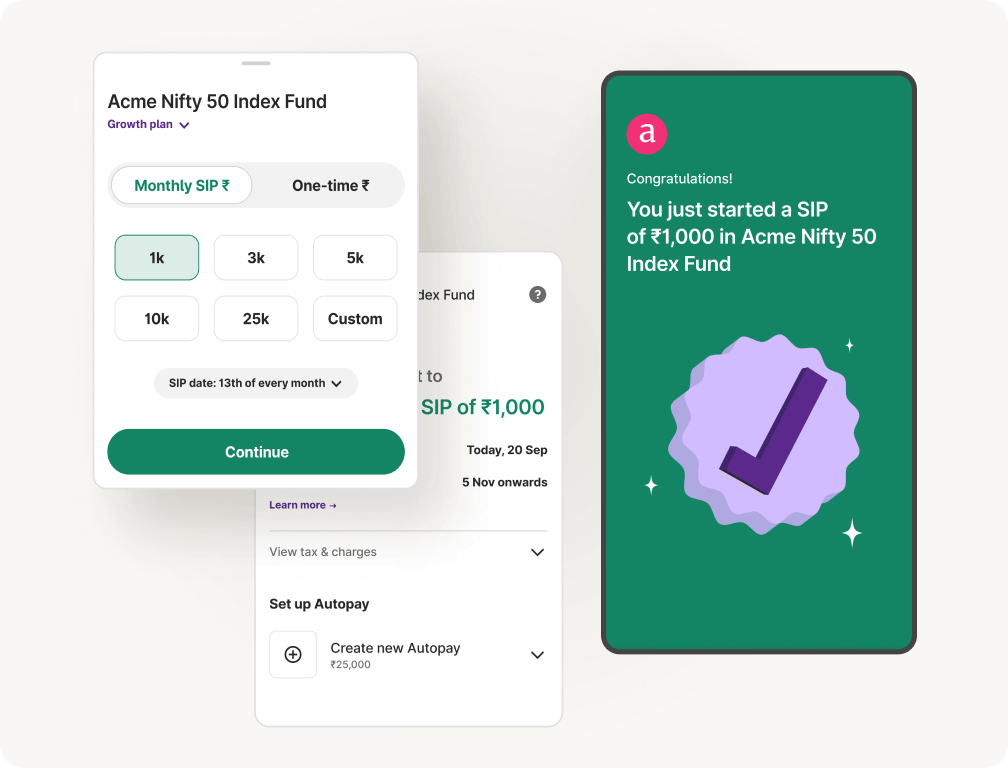
Open 24/7 | Pay via UPI | SIP mode for Stocks & Mutual Funds
Upstox Pro for Traders
Powerful trading in Equities, Futures, Options, Commodities and Currencies made simple
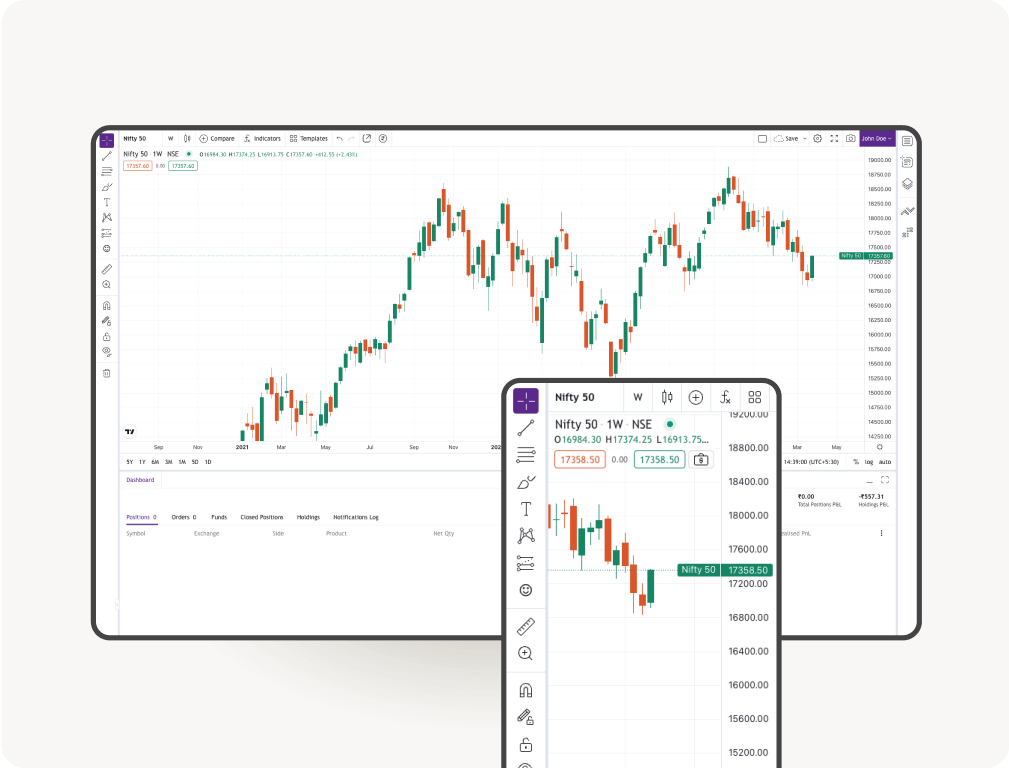
Powerful Charting
Powerful Discovery
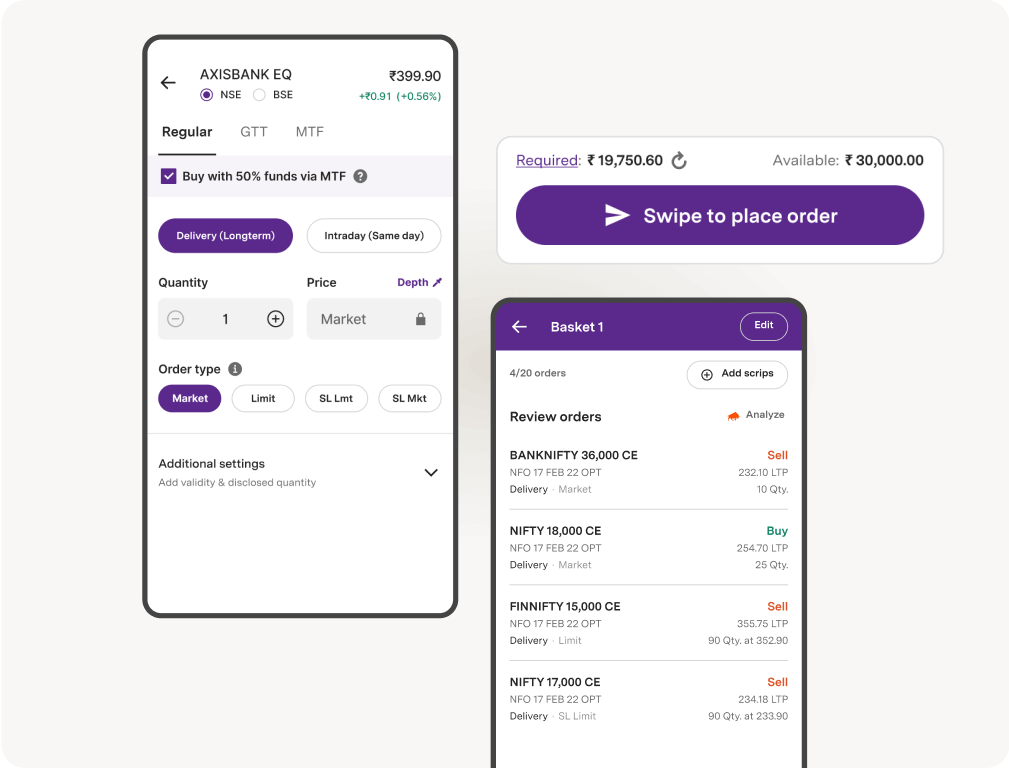
Powerful Execution
TradingView | 8 charts at once | 100+ indicators | 80+ Drawing tools
OI analysis | Option chain with greeks | FII & DII data | F&O smartlists

GTT | Basket orders up to 10 legs | 2X margin via Margin Pledge on 450+ stocks
Learn all about the Stock Market
With our jargon-free and expert-led Courses, Webinars, Events and self-help Videos
Transparent pricing.
No hidden charges.
*ZERO AMC is applicable for newly onboarded customers in the first year
Account Opening
Demat + Trading Account Charges
AMC*
Account Maintenance Charges
Commissions
For Mutual Funds and IPOs
Brokerage*
For Equity, F&O, Commodity and Currency Trades
Calculate Brokerage & Margin Easily With These
Explore All Calculators
Latest News
Get the Latest Market News at Your Fingertips
Don't take our word for it






