Market News
NIFTY50 to maintain a streak of positive closing for the 9th consecutive year; here’s why
.png)
5 min read | Updated on December 17, 2024, 18:14 IST
SUMMARY
The NIFTY50 has closed positively for eight consecutive years and is poised to extend its winning streak for a historic ninth year. This milestone highlights India's strong economic growth and key policy reforms like GST, corporate tax cuts, and infrastructure focus. Despite challenges such as the pandemic and global uncertainties, robust earnings growth and rising retail participation have driven its steady rise.

NIFTY50 to maintain a streak of positive closing for the 9th consecutive year; here’s why
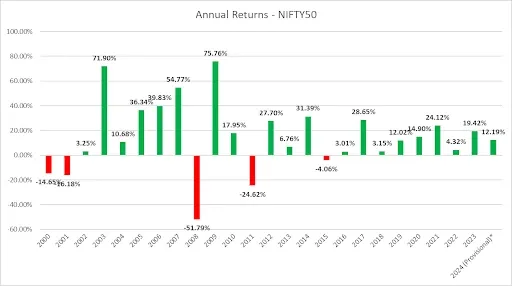
The NSE benchmark index NIFTY50 has shown it is on the verge of achieving a feat which is going to be historic. It’s on its way to extending its winning streak for the ninth straight year. In 2015 the NIFTY 50 was trading around 8,000, and today it is trading near the 24,400 level with absolute returns of 200% in the last 9 years.
This has been the longest yearly winning streak of closing in green for NIFTY50 since its inception. In the last 10 years, the calendar year of 2014 marked the highest gains of 31.39%, while in the last 24 years, NIFTY50 has shown a 75.76% jump in the year 2009. The year 2020 recorded the highest volume of 16,653 crore.
Source: Tradingview
GDP Growth
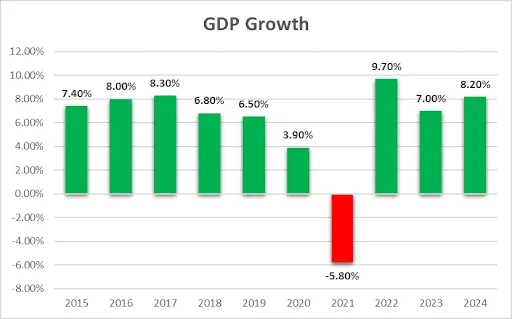
India's economy grew by 93%, from $2.04 trillion in 2014 to nearly $3.89 trillion in 2024. Besides, in the fiscal year ending March 2024, real GDP grew 8.20%. As one of the largest economies in the world, India's growth reflects its expanding technology sector, increasing foreign investment, and a growing middle class. (IBEF: Press Information Bureau)
Over the last 10 years, India's economy witnessed five phases. The Stable Phase (2014-2016) saw robust GDP growth (6.4%-8.3%) driven by domestic consumption, government spending, and favourable global conditions. The Structural Reforms Phase (2016-2017) included demonetisation and GST implementation, causing short-term disruptions and slowing growth to 7%.
The Economic Slowdown Phase (2018-2020) featured reduced demand, financial sector issues, and a manufacturing slump, lowering growth to 4.0%. The Global Pandemic Phase (2020-2021) saw GDP contract by 7.3% due to COVID-19 disruptions. In the Pandemic Recovery Phase (2021-2024), growth rebounded to 8.9% (2021-22) and 7.2% (2022-23), supported by domestic demand and services recovery.
Earnings of NIFTY50 in the last 10 Years
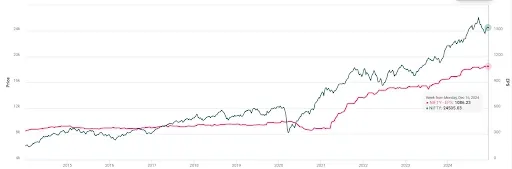
NIFTY50 and its EPS from January 2014 to December 16, 2024
Currently, the EPS of NIFTY50 is ₹1,072.90. From the calendar year 2014 to the 2020 Covid crash, the earnings growth remained stagnant. After 2020 and the impact of COVID-19 and lockdown the earnings dipped with the NIFTY50.
As the changes in government policies showed a positive effect, the markets picked up with strong earnings growth. The awareness of the market increased heavily in the same period expanding the market participation of retail investors. Since last January 2014, the EPS of NIFTY50 has shown growth of 218.06%.
Major policy changes in the last 10 years
In 2016 Indian Government announced demonetisation to which stock market reacted negatively due to uncertainty and economic disruptions it caused. However, in the long term, it was seen as a step towards formalising the economy and curbing black money. In 2017 the government implemented Goods and Services Tax (GST).
GST unified India's indirect tax system, simplifying the tax structure and reducing compliance costs. This led to improved ease of doing business, boosting investor confidence and positively impacting sectors like manufacturing and logistics. Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) in 2016 streamlined the insolvency resolution process, making it easier to recover bad loans and improve the health of the banking sector.
In 2019, the government reduced the corporate tax rate for domestic companies, making India one of the most competitive countries for business. This attracted foreign investment and positively impacted the stock market, particularly for companies in the manufacturing and services sectors.
The launching of Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Schemes incentivised domestic manufacturing in key sectors like electronics, pharmaceuticals, and automobiles. This has attracted significant investment and boosted the stock prices of companies in these sectors.
The government's major focus on infrastructure development, including roads, railways, and ports, has created opportunities for companies in these sectors. Reforms in the financial sector, like the consolidation of public sector banks and the strengthening of regulatory frameworks, have improved the health of the banking sector and increased investor confidence.
These policy changes have significantly impacted the Indian stock market and investor sentiment.
Major Events
2014-2019 :Bull market and economic reforms
The period of 2014 to 2019 India witnessed a notable bull market for the NIFTY50. The Indian economy experienced positive momentum due to various economic reforms, such as the introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) and the demonetisation process. Throughout this phase, the Nifty 50 achieved record levels, fueled by impressive corporate profits, solid economic expansion, and heightened investor optimism.
2020-2022: Pandemic impact and recovery
The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 caused widespread market disruptions, with the Nifty 50 experiencing a sharp decline in early 2020. However, the index demonstrated resilience and a quick recovery, supported by government stimulus measures, vaccine rollouts, and a rebound in economic activity.
2023-Present :A tale of two narratives
In 2023, the NIFTY50 hit the 21,000 mark for the first time and in 2024 it kept on hitting new milestones one after another. It made a peak above the 26,000 mark, however, in the latter part of the year, disappointing earnings and record selling by the FIIs led to apprehension in the markets. Despite these challenges, the index is on its way to mark the ninth consecutive year of gains.
About The Author
Next Story

