Join 1.3 Crore+ Indians
who trust us for
who trust us for
Trading & Investing
4.5+
Avg. app rating- Backed by the Best
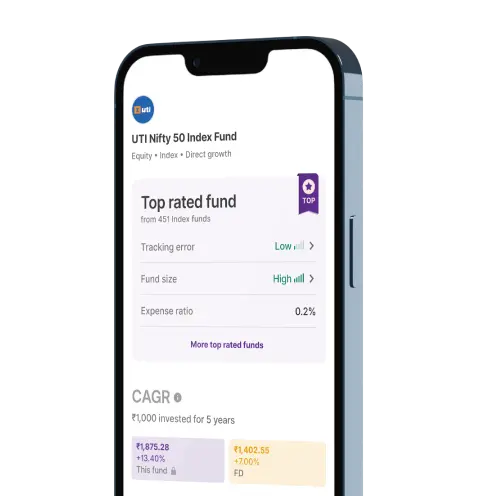
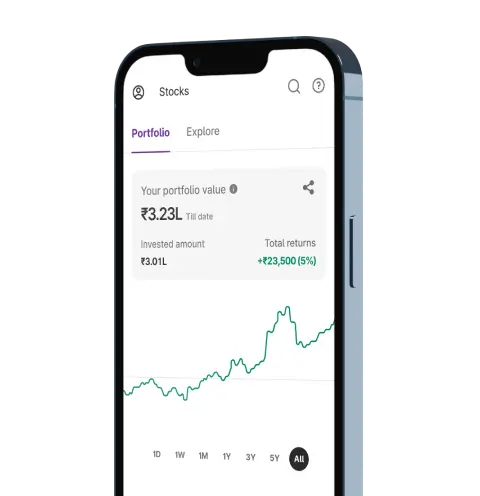
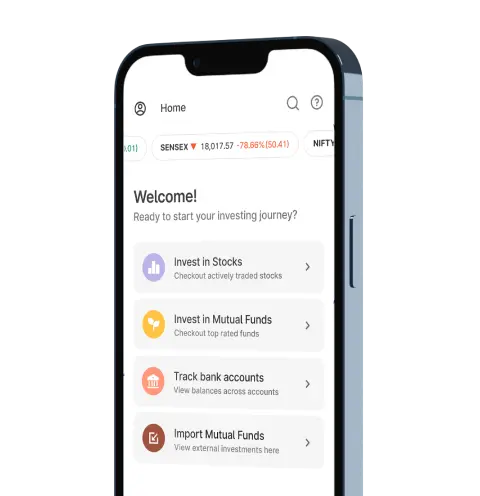
Upstox for Investors
Invest Right, Invest Now in Stocks, Mutual Funds, and IPOs
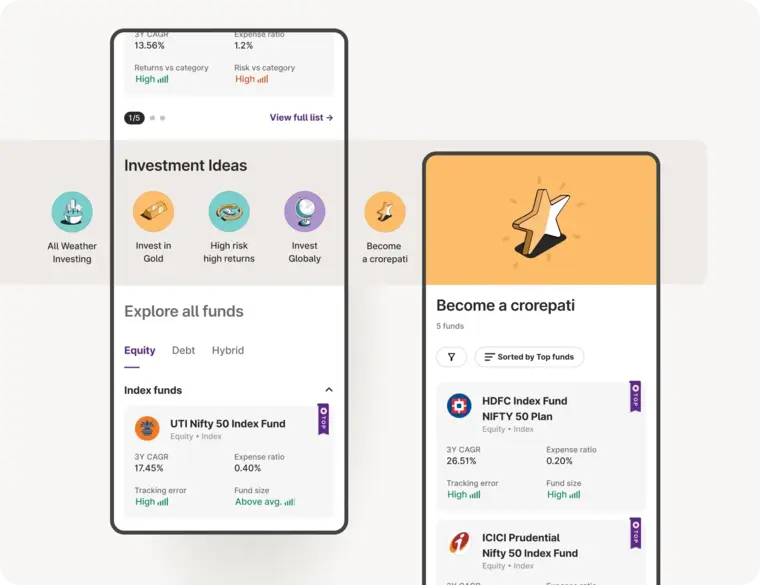
Investment Ideas
News & Insights
Order Placement
Top rated Funds | Best for Beginners | Top 30 actively traded Stocks
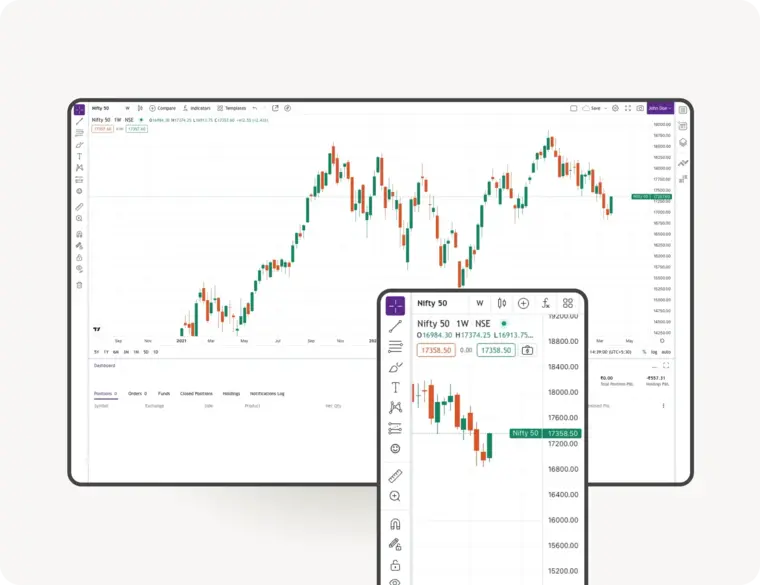
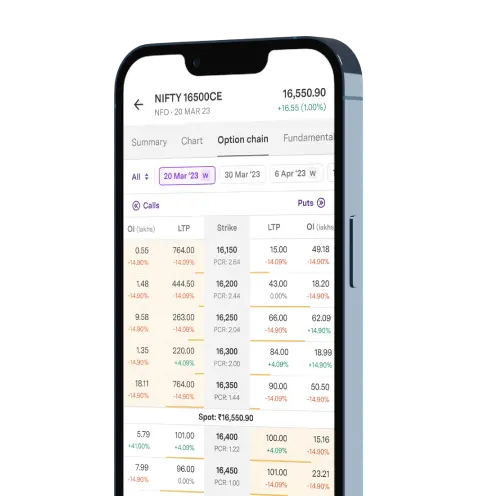
Upstox Pro for Traders
Powerful trading in Equities, Futures, Options, Commodities and Currencies made simple
Powerful Charting
Powerful Discovery
Powerful Execution
TradingView | 8 charts at once | 100+ indicators | 80+ Drawing tools