Upstox Originals
The rise of India’s digital backbone: Data centres at the forefront
.png)
6 min read | Updated on December 17, 2024, 17:48 IST
SUMMARY
Data consumption in India is growing exponentially! By the end of this decade, India is expected to reach 90% internet penetration. Despite this, India hosts only 2% of the world's data centres. As a backbone to our digital growth, data centres growth is vital not the data usage as well as safety! From big-city hubs like Mumbai to surprising opportunities in Tier 2 towns, this is the inside scoop on why India’s becoming the next global data hotspot.

By 2032, India's data centre industry is projected to reach $11.6 billion
Did you know that the average monthly data usage per user in India shot up to 24 GB in 2023, a 24% jump from 19 GB in 2022?
And this is just the start
A report by Ericsson Mobility (June 2023), suggests that India will be global leader in data consumption, which is expected to reach a whooping 62 GB of data per month, outpacing markets like the US, Western Europe, and China.
Ohh wait, we are not done yet!
India’s cloud market is also on a fast track, expected to grow at an impressive 23.8% CAGR from 2023 to 2028. Goes without saying, if India expects to reach these lofty targets, it will also need to build a solid backup infrastructure to support this growth.
Enter - Data centres
What is a data centre?
A data centre is like a high-tech fortress where servers, storage systems, and network gear work nonstop to handle data. It’s built to keep things running 24/7, with backup power, super-efficient cooling, and blazing-fast connectivity.
What’s happening in India’s data centre market?
As of 2023, the data centre market was worth about $4.5 billion, but that’s just the beginning. By 2032, it’s projected to more than double, reaching $11.6 billion, with a steady growth rate of approx 11% CAGR.
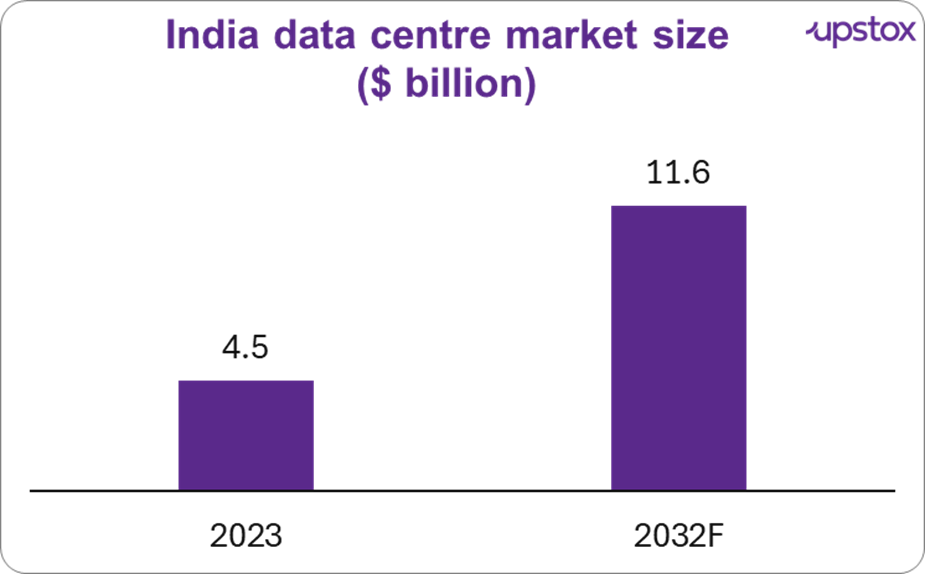
Sources: IBEF
Mumbai has emerged as a major data centre hub in Asia Pacific due to its strategic advantages, including the largest number of undersea cables and cable landing stations, as well as a highly developed ecosystem of carriers, content, and cloud.
The table below presents the data on India’s Data Centre Capacity (in MW) for the major 7 cities in 2023. These cities collectively contribute over 90-95% of the nation’s total data centre demand and supply, with Mumbai and Chennai leading the charge, accounting for ~60% of the share.
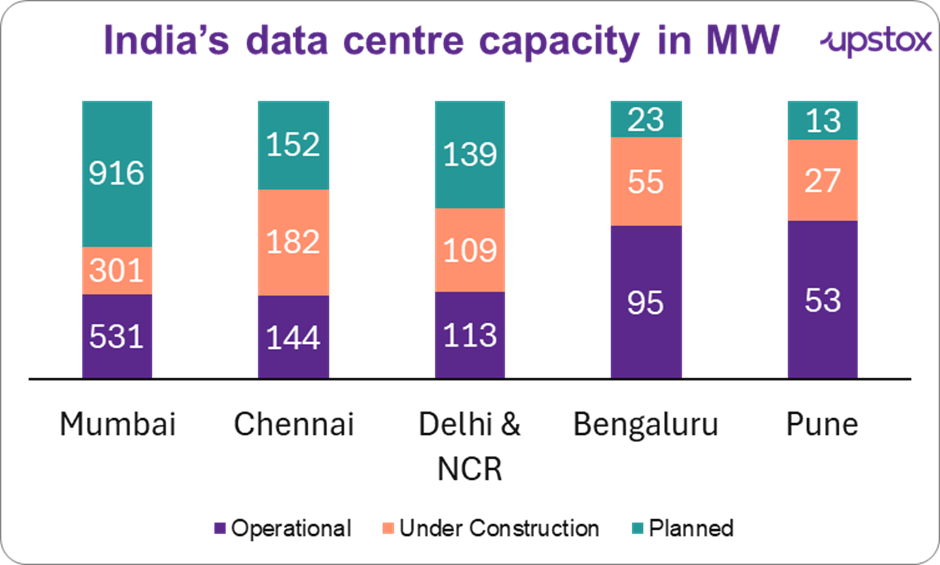
Source: C&W report, Industry, JM Financial
Factors driving this growth
-
Internet penetration - China leads with 1 billion internet users and a 77% penetration rate, while the USA has nearly 99%. India, with 0.7 billion users and a 50% penetration rate, is rapidly catching up. Driven by urbanisation, increased smartphone adoption, and digital initiatives, India is expected to reach a 90% penetration rate towards the end of this decade.
-
5G integration - The rollout of 5G in India has accelerated data consumption, with 5G users consuming 3.6x more data than 4G users.
-
Global connectivity - India's strategic location, coupled with investments in undersea cables and fiber networks, strengthens global data exchange. The growth of the data centre sector is driven by rising data traffic, technological advancements, and a supportive regulatory environment.
-
Affordable land costs - Lower land prices in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities attract data centres investments, offering cost-effective alternatives to Tier 1 hubs like Mumbai and Bengaluru.
Government initiatives
The government is also playing its role in proposing supportive regulations, which have fostered confidence in the market and increased investment. Key initiatives include:
-
Data Centre Incentivisation Scheme (DCIS): The proposed schemes aims to outline a range of fiscal and non-fiscal incentives for companies, encouraging the use of domestically manufactured equipment such as servers, storage systems, telecom and network devices, electrical components, and cooling equipment.
-
Data Centre Economic Zones (DCEZs): India plans to establish four dedicated zones, offering additional benefits and incentives to data centres within these zones.
Despite the advantages it offers, the data centre boom in India comes with a few risks that need to be managed to ensure long-term sustainability:
-
Security threats: Protecting sensitive data from hacking, malware, and phishing attacks is critical to prevent breaches and disruptions.
-
Energy and cooling: High energy consumption and heat generation require efficient power usage and cooling systems to avoid overheating and downtime.
-
Skilled workforce: Increasing demand for expertise in data analytics, cybersecurity, and cloud computing requires collaboration across industry, academia, and government to bridge the skills gap.
-
Modernisation: Older data centers often need upgrades to meet modern demands for processing power, efficiency, and scalability.
-
Environmental impact: High energy consumption, reliance on fossil fuels, water usage for cooling, and e-waste contribute to climate change, resource strain, and pollution. Additionally, heat released by cooling systems can create local micro-climates.
While this is definitely a space to look out for, there are no pure-play listed opportunities yet. However, below are some key players and their major shareholders
Major players in the Indian data centre market are:
| Company | Netmagic NTT | Nxtra by Airtel | Adaniconnex | L&T cloudfiniti | Sify | Techno Electric & Engineering |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Key Shareholder | NTT Data (Japan) | Airtel (76%), Carlyle (24%) | Adani Enterprises(50%), Edge Connex (50%) | Promoters (63%), | Promoter (84%), | Promoters |
| Operational Assets | 18 | 12 | 1 | NA | 12 | NA |
| Operating Capacity (MW) | 265 | 198 | 17 | NA | 108 | NA |
| Upcoming Capacity (MW) | 145 | 239 | 487 | 90 | 250 | 24 |
Source: Avendus
However, there is a silver lining While an investor can't directly invest in data centres (yet!), they can indirectly participate via a proxy play - real estate!
India's rapidly growing data center industry is closely tied to its real estate sector. To realise this potential, collaboration among government bodies, developers, and industry stakeholders will be vital in scaling eco-friendly data centers.
For the real estate sector, this expansion presents an opportunity to align with sustainability goals, boost rental yields, and deliver economic benefits to stakeholders.
Conclusion
Digital adoption in India is expected to grow by leaps and bounds! With technology becoming affordable, participation from rural India is also expected to spike sharply, adding to the existing load from urban India.
As such, data centres play a vital role in supporting this growth, while also ensuring data safety. While there are no direct investment opportunities, yet, this is definitely a sector to watch out for!
About The Author
Next Story
