Upstox Originals
Budgeting for change: India’s transformation in numbers
.png)
6 min read | Updated on January 28, 2025, 19:00 IST
SUMMARY
India’s Union Budgets from 2010 to 2024 highlight a transformative journey driven by evolving economic priorities. This period saw increased public expenditure focusing on modernisation and infrastructure. Fiscal policies balanced growth and sustainability amid global challenges and domestic needs. The article explores key budget highlights and their role in shaping national progress.

Infrastructure and defence have seen a sharp rise in their budget spends in the union budget
India’s union budget is scheduled for February 1, 2025 and everyone has certain expectations (and dare we say even aspirations) for what the budget will deliver. That said, in this article we look at how budget spend has evolved over the past decade and a half (since 2010, simply put).
The total expenditure of India's Union Budgets from 2010 to 2024 encapsulates a period of significant financial evolution, highlighting the country's strategic priorities. Over these years, public spending has dramatically increased, reflecting ambitious goals in modernisation and infrastructure development.
Public spending: A reflection of economic ambitions
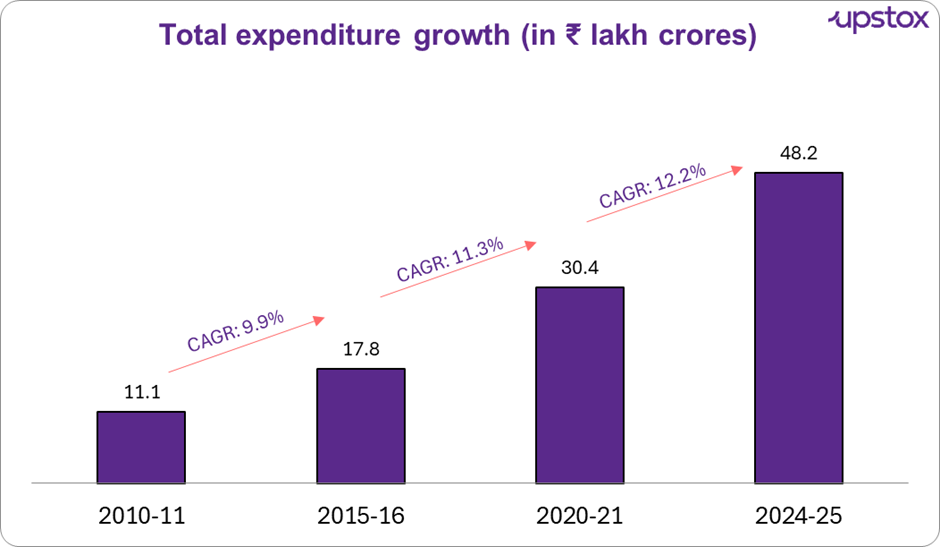
Source: News articles, The above is the budgeted spend for the relevant years
India's expenditure has significantly increased over the years, reflecting its growing ambitions. From 2010-11 to 2015-16, spending grew by over 60%, focusing on infrastructure and rural development. During the pandemic in 2020-21, the budget surged by over 70% to support relief efforts. The projected spending for 2024-25 shows a nearly 60% increase from 2020, with a strong focus on capital investments to drive long-term growth.
Evolving budget allocations: The shifting focus
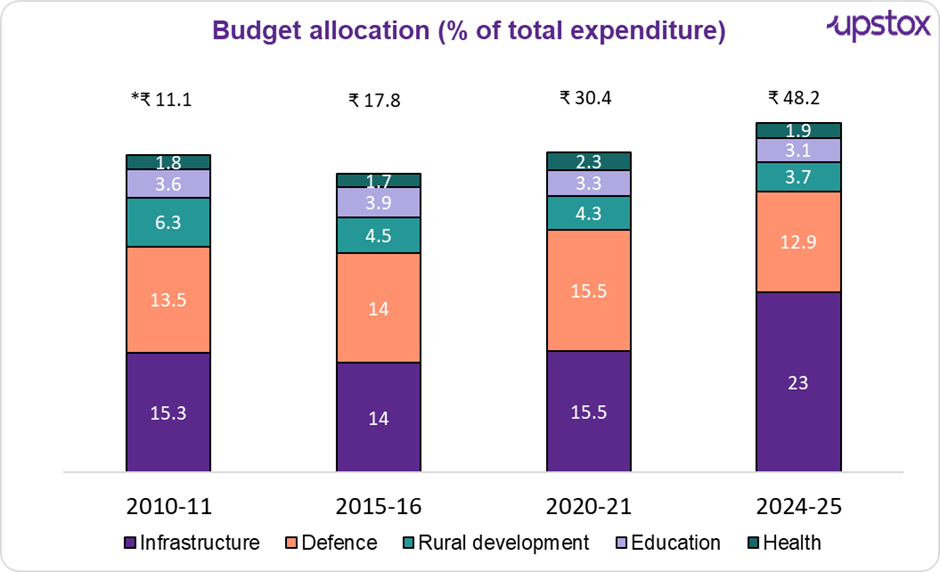
Source: News articles,*total budget expenditure in ₹ lakh cr,
Budget allocation to select sectors (₹ lakh cr)
| Sector | 2010-11 allocation | 2015-16 allocation | 2020-21 allocation | 2024-25 allocation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | 1.7 | 2.5 | 4.7 | 11.1 |
| Defence | 1.5 | 2.5 | 4.7 | 6.2 |
| Rural development | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1.3 | 1.8 |
| Education | 0.4 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 1.5 |
| Health | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
Source:News articles, The above is the budgeted spend for the relevant years
Evolving budget priorities
Defence
India’s defence budget highlights a focus on modernisation and domestic production, despite declining GDP shares from 2.1% in 2010-11 to 1.9% in 2024-25. The 2010-11 allocation was ₹1.47 lakh crore, with ₹60,000 crore for capital upgrades. By 2024-25, ₹6.22 lakh crore allocation prioritises operational readiness and domestic procurement under Aatmanirbharta.
Education
From ₹52,000 crore in 2010-11 to ₹99,300 crore in 2020-21, education funding saw significant growth, supported by initiatives like the Right to Education Act, 2009 and National Education Policy, 2020. Besides that increased funding for educational initiatives in rural areas, including the Pradhan Mantri Schools for Rising India (PM SHRI) launched in 2022.
Infrastructure
India’s Union Budgets 2010 to 2024 showcase a remarkable 540.2% increase in infrastructure allocation. In 2010-11, infrastructure accounted for 46% of the total plan allocation, focusing on road transport, railways, and rural development. By 2024-25, the emphasis shifted towards sustainable growth, with substantial funding boosts for railways and transformative initiatives like PM Gati Shakti.
Health
In 2010-11, ₹22,300 crore was allocated, focusing on AIDS control and infrastructure. By 2024-25, the allocation surged by 304.4% over the 14 years, benefiting programs like the National Health Mission and Ayushman Bharat. Despite this growth, health spending remained around 2% of GDP in 2024-25 compared to 1.1% in 2010-11, falling short of the 2.5% target.
Rural development
Rural development in India’s Union Budget aims at enhancing village life through better roads, clean water, electricity, improved healthcare and education, and job creation with programs like Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGA). From 2010 to 2024, there's been a notable rise in funding for rural development, growing from ₹66,100 crore to ₹1,22,398 crore in 2020-21, focusing on MGNREGA and Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana.
The 2024-25 budget continued this trend with a 70% increase in funding for the housing scheme, aiming to build three crore homes and launch Phase IV of the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana for better rural connectivity.
Fiscal policies: The tug of war between growth and sustainability
Now that we have learned about government spending, it is important to know about the Fiscal deficit.
In a nutshell,
-
The budget lays out the inflow and outflow of money into the government accounts
-
The fiscal deficit is the extra money that the government borrows when it spends more than it earns
Why should you care about this?
This metric is crucial for understanding the financial health of the country. In one way or the other, the government’s fiscal deficit efforts will determine a lot of economic activity. Let’s take a few examples:
-
If the deficit widens, the government might need to borrow more money (they need to fund their expenses one way or the other) which puts pressure on the interest rates.
-
If, for example, the government wants to lower the fiscal deficit, they may decide to cut their spending quite a bit. This could impact overall growth in the economy.
India's fiscal policies have evolved over the years. The Union Budgets from 2010-11 to 2024-25 demonstrate a trajectory of fiscal consolidation efforts
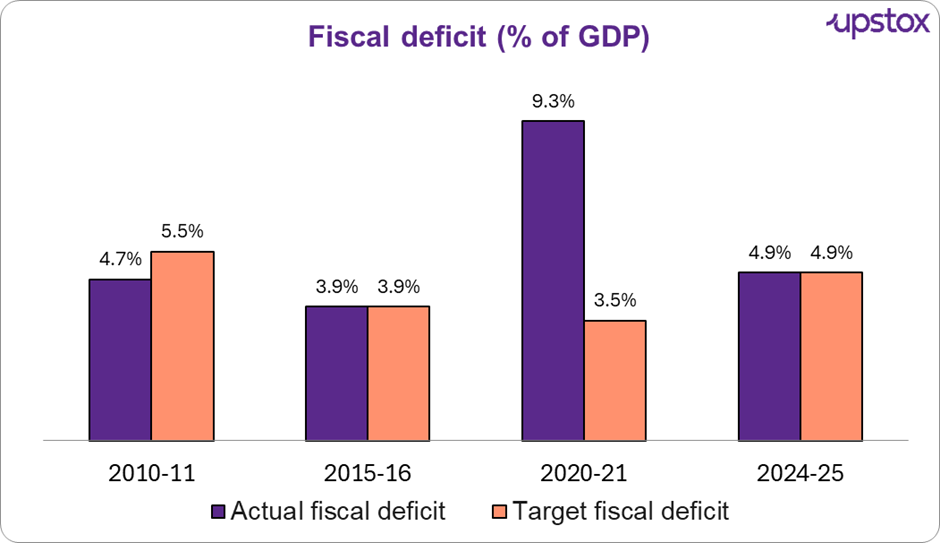
Source: News articles; *2020-21 deficit was high due to COVID-19
India’s fiscal deficit trajectory from 2010 to 2024 highlights the country’s efforts to balance economic priorities amidst varying challenges. In 2010, due to higher than estimated tax and non-tax revenues, the actual fiscal deficit figure was lower than the estimated figure of 5.5%.
The pandemic in 2020 disrupted this trend, causing the fiscal deficit to soar to 9.3%—far exceeding the 3.5% target. The sharp rise resulted from reduced tax revenues and increased expenditure on healthcare, welfare, and economic stimulus measures during the crisis. The government’s borrowing surged to bridge the gap, underscoring the strain on fiscal health.
By 2024, India successfully restored fiscal stability, achieving a deficit that aligned with the planned 4.9% deficit.
Outlook
The upcoming Indian Union Budget 2025 is expected to bring changes across different areas that affect people’s lives.
-
In defence, the government may focus on making more equipment in India instead of buying from other countries. Case in point, over the past few days, India commissioned three naval ships on the same day, all of them were Made in India. This focus is expected to persist.
-
For education, there’s hope for more money to help people learn new skills and get better at their jobs. Some think there should also be lower taxes on school supplies and special tax breaks for students from poor families.
-
In infrastructure, we might see plans to build more using clean energy and green technology, with rewards for people investing in eco-friendly projects. In health, making medical devices cheaper by reducing taxes could help hospitals and patients save money.
-
For rural areas, the government might invest in smart farming tools like satellite data and artificial intelligence to help farmers grow more food.
By signing up you agree to Upstox’s Terms & Conditions
About The Author
Next Story
